The human body system produces hormones which are chemicals passing messages from one part of the body to another. They travel in the bloodstream to tissues and organs to regulate physiology and behaviour and maintain homeostatis. Hormones are classified by their chemical nature, mechanism of action, nature of action, their effects and stimulation of the endocrine glands.
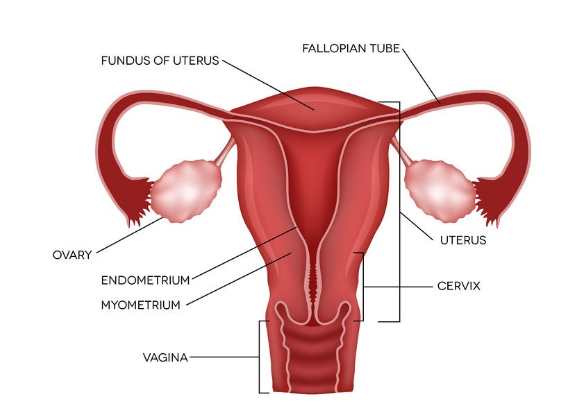
Estrogen is chiefly a female hormone because it is mostly secreted in the ovaries, a small proportion is secreted by the adrenal glands located above the kidneys and the body fat tissue in both men and women. The body makes three main types of estrogen and its most potent form is called estradiol – this has a similar function to the male hormone androgen. Estrogens are a group of sex hormones which promote the development and the maintenance of the primary and secondary female sexual characteristics.
At the onset of puberty, estrogen plays a role in the development of female secondary characteristics like the breasts, wider hips and pubic hair. This chemical messenger helps regulate menstrual cycle. If an ovum – the woman’s egg- is not fertilized, there’s a sharp drop in estrogen and menstruation occurs.
If the ovum is fertilized, estriol, a type of estrogen works with progesterone (another hormone) to stop ovulation during pregnancy. Estrogen plays a role in every part of your reproductive life from puberty to menopause. Both estrogen and progesterone begin to decline around your late 30s.
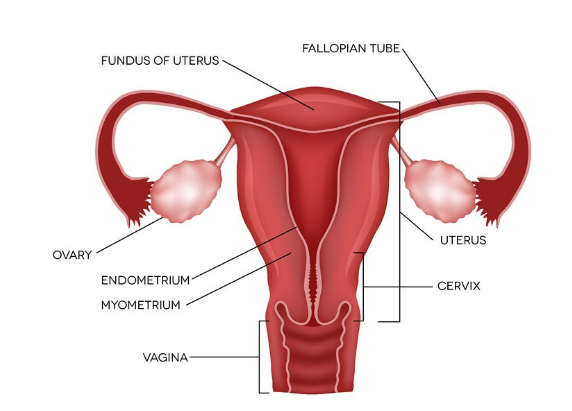
Estrogen is an essential chemical in bone formation. It works with vitamin D, calcium and other hormones to effectively break down and rebuild bones according to the body’s natural processes. As estrogen levels start to decline in middle age, the process of rebuilding bones slows, with postmenopausal women eventually breaking down more bone than they produce.
Cleveland Clinic says this is why postmenopausal women are four times more likely to suffer from osteoporosis than men. Bone metabolism is influenced by sex steroids during growth and adulthood in both men and women. Estradiol levels are strongly associated with bone mineral density (BMD), bone turnover and bone loss than testosterone levels in adult men. Levels of estradiol in elderly men are higher than those in postmenopausal women.
This female hormone also plays a role in blood clotting, maintaining the strength and thickness of the vaginal wall and the urethral lining, vaginal lubrication and a host of other bodily functions.
It even affects skin, hair, mucous membranes and the pelvic muscles, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine. For example, estrogen can make the skin darker. Some researchers hope to use this information to create safe fake tanning lotions by activating the skin darkening. Other functions of estrogen are in the control of cholesterol, affects the brain and mood, heart and other tissues.
Your body works the way it should, when the hormones are balance but when they are not balanced several health issues can arise. When you have an excess of amount Estrogen you may have
• Weight gain, mainly in your waist, hips, and thighs
• Menstrual problems, such as light or heavy bleeding
• Worsening of premenstrual syndrome
• Fibrocystic breasts (non-cancerous breast lumps)
• Fibroids (noncancerous tumors) in the uterus
• Fatigue and memory problems
• Loss of sex drive
• Depressed or anxious feelings
Low estrogen can result in menstrual migraine. Some women experience a terrible headache right before their menstrual period, because of drop in estrogen level. However, the common reason for low estrogen in women is menopause or surgical removal of the ovaries. When you produce a low amount of this hormone your symptoms will include:
.
• Menstrual periods that are less frequent or that stop
• Hot flashes (suddenly feeling very warm) and/or night sweats
• Trouble sleeping
• Dryness and thinning of the vagina
• Low sexual desire
• Mood swings
• Dry skin
In men excess estrogen can result in enlarged breasts (gynecomastia), poor erections and infertility. While excess belly fat and low sexual desire are the effect of drop in estrogen levels in men.
Treatment with estrogen.
Estrogen is an ingredient of most oral control pills. Since this hormone helps pregnant women not to ovulate, birth control pills mimic this effect by regulating the levels of estrogen. Menopausal women opt for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to treat hot flushes, sleeping problems, vagina dryness etc. According to the University of California says estrogen and androgen have been used for over 50 years as an effective in treatment gender dysphoria.
There are risks like stroke, breast cancer and blood clots caused by the administration of this treatment that it is better administered on case-by-case bases. However it is currently approval for post menopausal symptoms, The Food and Drug Administration (FAO) warns that women who start hormone replacement therapy are encouraged to try the smallest dose for the shortest amount of time. Only women with severe risk of osteoporosis who cannot take non-estrogen therapies should be considered for using hormone replacement therapy preventively.